What is x402?
The x402 is an open protocol for internet-native payments. The 402 Error code stands for "Payment Required" and existed for a long time in the HTTP specs, but only now it became feasible to use thanks to the rise of blockchain networks. Now 402 protocol refers to implementing the HTTP 402 Payment Required pattern: the server requires a payment before returning a protected response. On Solana, this is commonly implemented by asking the client to submit a small transfer, then the server verifies this on-chain and serves the content.
At the moment it is not yet clear which of the 402 SDKs will be the most popular. So in this guide we will show how to implement x402 using a minimal server and client and list all the available 402 SDKs with the current Solana support described.
How does it work?
There are several ways to implement x402, ranging from super-lean to fully managed.
Protocol idea: Use plain HTTP. A client hits your URL → you reply 402 Payment Required with a JSON Payment Requirements object → the client pays and retries with an X-PAYMENT header → you verify/settle → respond 200 OK. No accounts, no OAuth.
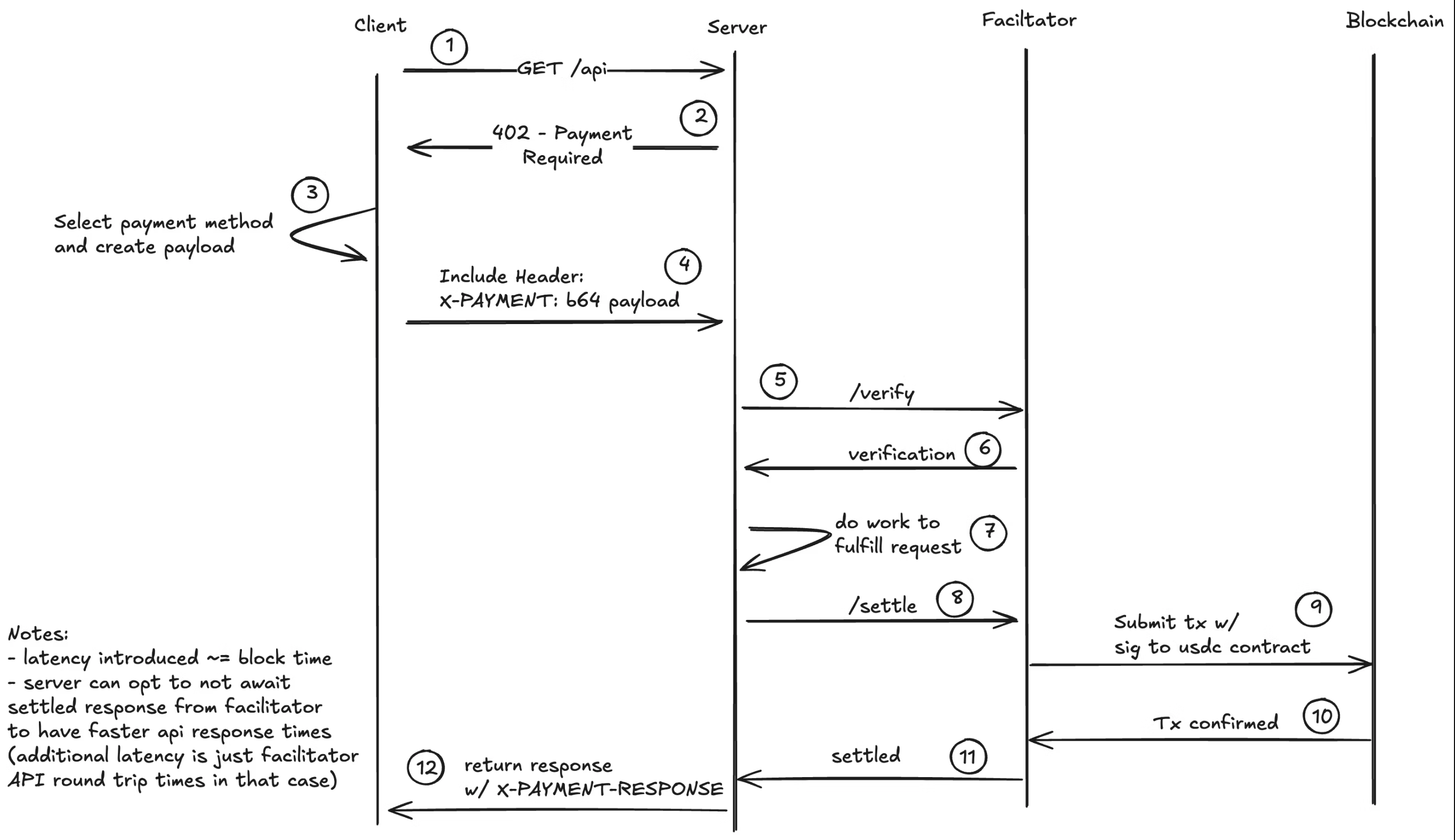 x402 Flow Diagram
x402 Flow Diagram
Note: The facilitator is completely optional and you can also implement your own validation logic with a few lines of code. The facilitator abstracts the blockchain integration details from the server and client which makes it easier to implement.
Spec bits to know: The PaymentRequirements structure, base64-encoded
X-PAYMENT header, optional X-PAYMENT-RESPONSE on success, and the (optional)
facilitator API for /verify, /settle, /supported. Current concrete scheme is
exact (pay a specific amount). Others like upto are proposed.
Solana support: The protocol itself is chain-agnostic; on Solana it supports all SPL tokens. Solana support is available or in development for most 402 SDKs.
Further down is a list of the available 402 SDKs with their current Solana support.
Use Cases
x402 enables a wide range of micro payment and pay-per-use scenarios that weren't economically feasible before blockchain. Imagine Netflix paying for each view or Spotify paying for each song instead of paying for subscriptions. Here are a few possible ideas. But the whole spectrum of possibilities is open to imagination:
AI & Agent Commerce:
- AI Agent API Access: Pay per LLM inference, image generation, or AI model API call (See ACK example)
- MCP Server Monetization: Charge for Model Context Protocol tools, data sources, and specialized agent capabilities (See MCPay.tech)
- Agent-to-Agent Payments: Enable autonomous agents to transact with each other for services and data (See a2a-x402 example)
- Premium AI Training Data: Sell access to curated datasets on a per-query basis
Content & Media:
- Paywalled Articles: Charge micro-amounts per article instead of full subscriptions
- Video/Audio Streaming: Pay per view or per minute of content
- High-Resolution Images: Unlock full-resolution downloads after payment (see ACK example) or x402 coinbase example
- Premium Newsletter Access: Monetize individual newsletter issues
Developer Services:
- API Metering: Pay per RPC call, database query, or compute unit (See Corbits example)
- Serverless Functions: Charge for individual function executions
Data & Analytics:
- Real-Time Market Data: Per-quote or per-tick pricing feeds
- Analytics Dashboards: Unlock specific reports or data exports
- IoT Sensor Data: Micropayments for sensor readings from DePIN networks
Gaming & Virtual Goods:
- Game Server Access: Pay per session or per hour
- Mod/Asset Downloads: Monetize user-generated content
- Tournament Entry Fees: Automated prize pool distribution
Miscellaneous:
- Email/DM Filtering: Require payment to reach your inbox (spam prevention)
- Compute Resources: Pay per CPU hour, GPU minute, or storage GB
- VPN/Proxy Access: Per-GB bandwidth pricing
- One-Time File Downloads: Sell digital files without subscription overhead (See ACK example)
The key advantage of x402 on Solana is low transaction costs (fractions of a cent) making true micro payments viable, plus instant settlement enabling real-time access control.
SDKs and their Solana support
This is an evolving list and will be updated as more SDKs are released or Solana support is added.
| SDK / Project | Solana support | Notes | Docs / URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corbits | Yes | Convenient SDK for 402 on Solana | Docs |
| MCPay.tech | Yes | Pay for MCP servers in micropayments | Website |
| PayAI Facilitator | Yes | x402 facilitator with solana support | payai.network |
| Coinbase | Yes / Python in progress | The coinbase reference implementation of the x402 protocol | GitHub |
| ACK | In PR | An agent payment protocol with x402 support | GitHub |
| Crossmint | In development | Payments, wallets; agentic finance; not x402-specific | crossmint.com |
| A2A x402 (Google) | In development | Agent-to-Agent payments using google ai | GitHub |
| Nexus (Thirdweb) | In development | x402 wrapper around API keys | Nexus |
| x402scan | N/A (Explorer) | x402 ecosystem explorer (not an SDK) | x402scan.com |
| Native Example | Yes | Minimal example without dependencies | Examples |
Corbits
Solana-first SDK to implement x402 flows quickly on Solana. See the docs: https://corbits.dev/
Example that lets you pay for Solana RPC requests.
npm install @faremeter/payment-solana @faremeter/fetch @faremeter/info@solana/web3.js
Create a payer-wallet.json and fund it with some USDC and some mainnet sol.
import {Keypair,PublicKey,VersionedTransaction,Connection} from "@solana/web3.js";import { createPaymentHandler } from "@faremeter/payment-solana/exact";import { wrap } from "@faremeter/fetch";import { lookupKnownSPLToken } from "@faremeter/info/solana";import * as fs from "fs";// Load keypair from fileconst keypairData = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync("./payer-wallet.json", "utf-8"));const keypair = Keypair.fromSecretKey(Uint8Array.from(keypairData));const network = "mainnet-beta";const connection = new Connection("https://api.mainnet.solana.com");const usdcInfo = lookupKnownSPLToken(network, "USDC");const usdcMint = new PublicKey(usdcInfo.address);// Create wallet interfaceconst wallet = {network,publicKey: keypair.publicKey,updateTransaction: async (tx: VersionedTransaction) => {tx.sign([keypair]);return tx;}};// Setup payment handlerconst handler = createPaymentHandler(wallet, usdcMint, connection);const fetchWithPayer = wrap(fetch, { handlers: [handler] });// Call the API - payment happens automaticallyconst response = await fetchWithPayer("https://helius.api.corbits.dev", {method: "POST",headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },body: JSON.stringify({jsonrpc: "2.0",id: 1,method: "getBlockHeight"})});const data = await response.json();console.log(data);
npx tsx e2e.ts
This will pay for the RPC request and return the block height paying using corbits 402 protocol.
Coinbase
Coinbase's reference implementation of the x402 protocol provides TypeScript libraries and examples for both client and server flows. The repository includes end-to-end tests covering 6 different SVM (Solana Virtual Machine) scenarios. The implementation covers payment verification, receipt generation, and error handling.
Key features:
- TypeScript client and server implementations
- Payment verification utilities
- Support for multiple payment schemes (exact amount, up-to amount)
- Test suite with Solana transaction examples
- Separation between protocol logic and business logic
You can find an easy to use example with a minimal server and client here.
const app = express();const PORT = 3000;// Apply x402 payment middleware// This automatically handles:// - 402 responses with payment requirements// - Payment verification (pre-flight checks)// - Transaction submission via facilitator// - Settlement confirmationapp.use(paymentMiddleware(RECIPIENT, {// Protected endpoint: requires $0.001 USDC payment"GET /premium": {price: "$0.0001", // Price in USD (converted to USDC)network: "solana-devnet" // Solana devnet},// Another endpoint with different price"GET /expensive": {price: "$0.001",network: "solana-devnet"}}));// Protected endpoints - only accessible after paymentapp.get("/premium", (req, res) => {res.json({message: "🎉 Premium content accessed!",data: {secret: "This is premium content",timestamp: new Date().toISOString()}});});
Python support is in development with a working end-to-end example available here.
ACK
The Agent Commerce Kit (ACK) supports the x402 protocol but adds critical layers for the agent economy: verifiable agent identity (ACK-ID) using W3C DIDs/VCs and cryptographically secure receipts (ACK-Pay) as Verifiable Credentials. This allows agents to prove ownership, authenticate autonomously, and generate compliance-ready payment proofs addressing the identity crisis and transaction barriers that prevent AI agents from participating in commerce.
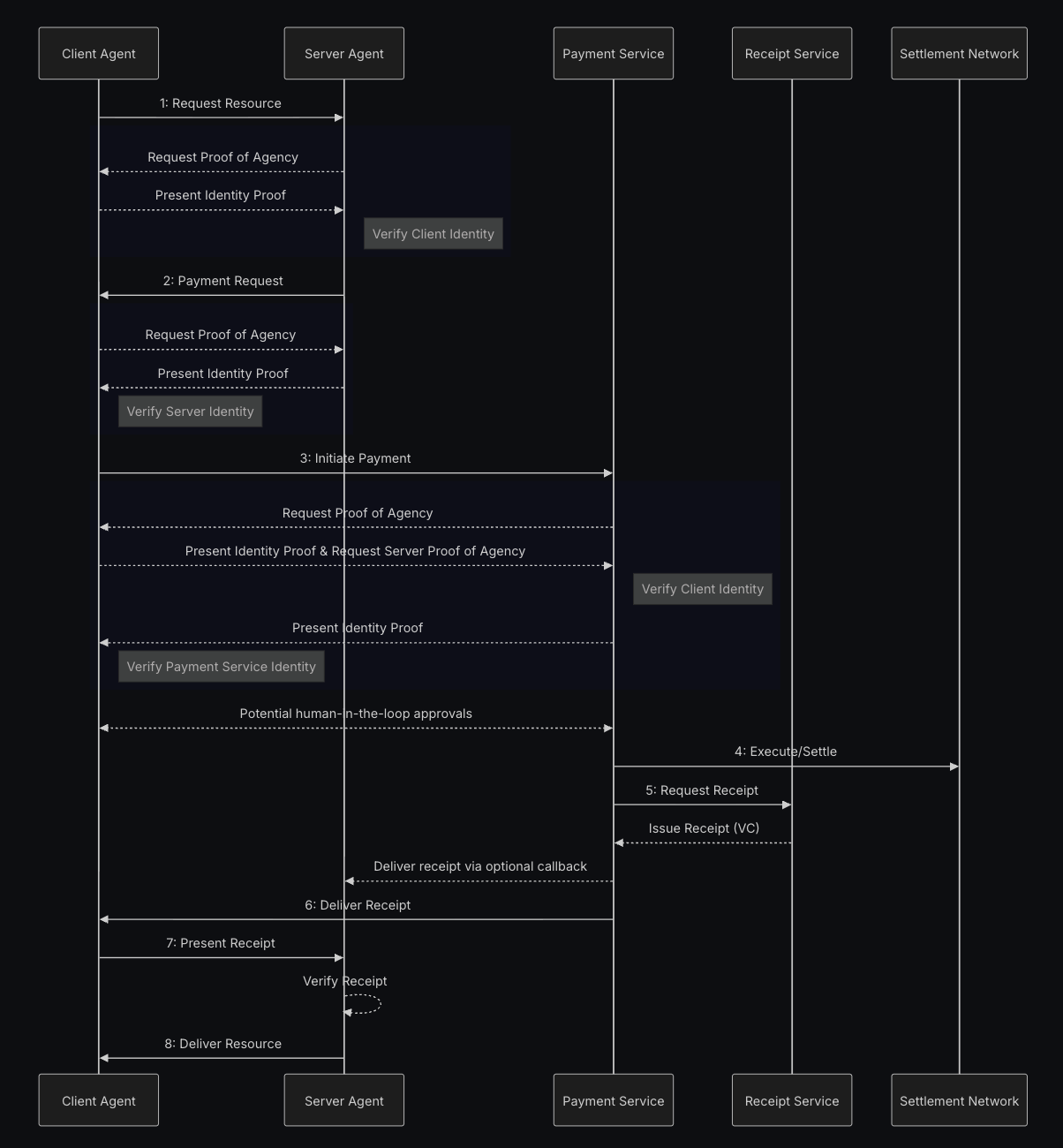 ACK Flow Diagram
ACK Flow Diagram
There is a PR with an e2e example that is not merged yet, but works. There is also a Live Example showing how to paywall images, a juke box and an API that can animate images. The source code for the examples together with a twitter bot using the api to animate images on the time line can be found here.
MCPay.tech
Pay-per-request micropayments for MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers using x402-like flows. Enables developers to monetize MCP tools and resources by requiring small payments for each API call or tool invocation, making it easy to charge for AI agent access to premium data sources, specialized tools, or computational resources. Site: https://mcpay.tech/
PayAI Facilitator
Solana-first x402 facilitator with a live echo merchant to test and refund payments. PayAI is at the moment taking over all transaction fees. Site: https://payai.network/
A2A x402 (Google)
Agent-to-agent 402 initiative exploring standardized payment-required flows. Solana support is currently in progress and a working chat example can be found here
Crossmint
Crossmint is an all-in-one platform for companies and agents to integrate crypto rails — including wallets, onramps, stablecoin orchestration, and more. Solana x402 support is currently in progress and is supposed to be finished by 30.10.2025. Site: https://www.crossmint.com/
x402scan
Explorer for the x402 ecosystem that provides comprehensive stats, project listings, and analytics for x402 implementations. Track transaction volumes, discover active merchants, and monitor the growth of payment-required endpoints across different networks. Site: https://x402scan.com/
Nexus (Thirdweb)
Thirdweb Nexus develops a x402 wrapper around API keys (currently in development). Site: https://nexus.thirdweb.com/
Native example
A native example without dependencies and with a minimal server and client.
You can clone the repository and run the example:
git clone https://github.com/Woody4618/x402-solana-examplesnpm install# Terminal 1: Start servernpm run usdc:server# Terminal 2: Run client (requires devnet USDC)npm run usdc:client
Flow Overview
- Client requests
/premium. - Server replies 402 with payment terms: recipient, amount.
- Client creates a transaction with a transfer instruction to the recipient.
- Client retries
/premiumwith the transaction payload. - Server verifies the transaction and sends the transaction to the network.
- Once it is confirmed, the server responds 200.
Solana-specific alternative: On Solana, you could implement a variant where the client submits the transaction directly to the network with a memo instruction (rather than sending it to the server), then sends just the transaction signature to the server for verification. This solves the connection-loss problem—if the client disconnects after payment but before receiving content, they can retry with the same signature since the payment is already confirmed on-chain. However, this approach deviates from the x402.org standard flow (which expects the server to broadcast the transaction), so we're using the standard approach in this example.
Note: The code of this example is not audited and is not production ready and is for demonstration purposes only. It shows that you can implement x402 without dependencies and the use of a facilitator. Using a facilitator is nice because they hide complexity and can take over transaction fees but they can also be a single point of failure, when the facilitator wallet runs out of funds for example. The example server submits client signed transactions. You may need to validate these.
Minimal Server (Express)
// x402-compliant server with USDC (SPL Token) paymentsimport express from "express";import { Connection, PublicKey, Transaction } from "@solana/web3.js";import { TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID, getAssociatedTokenAddress } from "@solana/spl-token";const connection = new Connection("https://api.devnet.solana.com", "confirmed");// Devnet USDC mint addressconst USDC_MINT = new PublicKey("4zMMC9srt5Ri5X14GAgXhaHii3GnPAEERYPJgZJDncDU");// Your recipient wallet address (same as SOL example)const RECIPIENT_WALLET = new PublicKey("seFkxFkXEY9JGEpCyPfCWTuPZG9WK6ucf95zvKCfsRX");// Derive the recipient's USDC token account (Associated Token Account)const RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(USDC_MINT,RECIPIENT_WALLET);// Picking a small USDC priceconst PRICE_USDC = 100; // 0.0001 USDCconst app = express();app.use(express.json());// x402 endpoint - Quote or verify paymentapp.get("/premium", async (req, res) => {const xPaymentHeader = req.header("X-Payment");// If client provided X-Payment header, verify and submit transactionif (xPaymentHeader) {try {// Decode base64 and parse JSON (x402 standard)const paymentData = JSON.parse(Buffer.from(xPaymentHeader, "base64").toString("utf-8")) as {x402Version: number;scheme: string;network: string;payload: {serializedTransaction: string;};};console.log("Received USDC payment proof from client");console.log(` Network: ${paymentData.network}`);// Deserialize the transactionconst txBuffer = Buffer.from(paymentData.payload.serializedTransaction,"base64");const tx = Transaction.from(txBuffer);console.log("Verifying SPL Token transfer instructions...");// Step 1: Introspect and decode SPL Token transfer instructionconst instructions = tx.instructions;let validTransfer = false;let transferAmount = 0;for (const ix of instructions) {// Check if this is a Token Program instructionif (ix.programId.equals(TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID)) {// SPL Token Transfer instruction layout:// [0] = instruction type (3 for Transfer)// [1-8] = amount (u64, little-endian)if (ix.data.length >= 9 && ix.data[0] === 3) {// Read the amount (u64 in little-endian, starts at byte 1)transferAmount = Number(ix.data.readBigUInt64LE(1));// Verify accounts: [source, destination, owner]if (ix.keys.length >= 2) {const destAccount = ix.keys[1].pubkey;if (destAccount.equals(RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT) &&transferAmount >= PRICE_USDC) {validTransfer = true;console.log(` ✓ Valid USDC transfer: ${transferAmount / 1000000} USDC`);console.log(` To: ${RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT.toBase58()}`);break;}}}}}if (!validTransfer) {return res.status(402).json({error:"Transaction does not contain valid USDC transfer to recipient with correct amount",details:transferAmount > 0? `Found transfer of ${transferAmount}, expected ${PRICE_USDC}`: "No valid token transfer instruction found"});}// Step 2: Simulate the transaction BEFORE submittingconsole.log("Simulating transaction...");try {const simulation = await connection.simulateTransaction(tx);if (simulation.value.err) {console.error("Simulation failed:", simulation.value.err);return res.status(402).json({error: "Transaction simulation failed",details: simulation.value.err,logs: simulation.value.logs});}console.log(" ✓ Simulation successful");} catch (simError) {console.error("Simulation error:", simError);return res.status(402).json({error: "Failed to simulate transaction",details:simError instanceof Error ? simError.message : "Unknown error"});}// Step 3: Submit the transaction (only if verified and simulated successfully)// Note: Solana blockchain automatically rejects duplicate transaction signaturesconsole.log("Submitting transaction to network...");const signature = await connection.sendRawTransaction(txBuffer, {skipPreflight: false,preflightCommitment: "confirmed"});console.log(`Transaction submitted: ${signature}`);// Wait for confirmationconst confirmation = await connection.confirmTransaction(signature,"confirmed");if (confirmation.value.err) {return res.status(402).json({error: "Transaction failed on-chain",details: confirmation.value.err});}// Fetch the transaction to verify payment detailsconst confirmedTx = await connection.getTransaction(signature, {commitment: "confirmed",maxSupportedTransactionVersion: 0});if (!confirmedTx) {return res.status(402).json({error: "Could not fetch confirmed transaction"});}// Verify token balance changes from transaction metadataconst postTokenBalances = confirmedTx.meta?.postTokenBalances ?? [];const preTokenBalances = confirmedTx.meta?.preTokenBalances ?? [];// Find the recipient's token account in the balance changeslet amountReceived = 0;for (let i = 0; i < postTokenBalances.length; i++) {const postBal = postTokenBalances[i];const preBal = preTokenBalances.find((pre) => pre.accountIndex === postBal.accountIndex);// Check if this is the recipient's accountconst accountKey =confirmedTx.transaction.message.staticAccountKeys[postBal.accountIndex];if (accountKey && accountKey.equals(RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT)) {const postAmount = postBal.uiTokenAmount.amount;const preAmount = preBal?.uiTokenAmount.amount ?? "0";amountReceived = Number(postAmount) - Number(preAmount);break;}}if (amountReceived < PRICE_USDC) {return res.status(402).json({error: `Insufficient payment: received ${amountReceived}, expected ${PRICE_USDC}`});}console.log(`Payment verified: ${amountReceived / 1000000} USDC received`);console.log(`View transaction: https://explorer.solana.com/tx/${signature}?cluster=devnet`);// Payment verified! Return premium contentreturn res.json({data: "Premium content - USDC payment verified!",paymentDetails: {signature,amount: amountReceived,amountUSDC: amountReceived / 1000000,recipient: RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT.toBase58(),explorerUrl: `https://explorer.solana.com/tx/${signature}?cluster=devnet`}});} catch (e) {console.error("Payment verification error:", e);return res.status(402).json({error: "Payment verification failed",details: e instanceof Error ? e.message : "Unknown error"});}}// No payment provided - return 402 with payment detailsconsole.log("New USDC payment quote requested");return res.status(402).json({payment: {recipientWallet: RECIPIENT_WALLET.toBase58(),tokenAccount: RECIPIENT_TOKEN_ACCOUNT.toBase58(),mint: USDC_MINT.toBase58(),amount: PRICE_USDC,amountUSDC: PRICE_USDC / 1000000,cluster: "devnet",message: "Send USDC to the token account"}});});app.listen(3001, () => console.log("x402 USDC server listening on :3001"));
Minimal Client (Node)
import { Connection, Keypair, PublicKey, Transaction } from "@solana/web3.js";import {createTransferInstruction,getOrCreateAssociatedTokenAccount,createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction,getAccount} from "@solana/spl-token";import fetch from "node-fetch";import { readFileSync } from "fs";const connection = new Connection("https://api.devnet.solana.com", "confirmed");const keypairData = JSON.parse(readFileSync("./pay-in-usdc/client.json", "utf-8"));const payer = Keypair.fromSecretKey(Uint8Array.from(keypairData));async function run() {// 1) Request payment quote from serverconst quote = await fetch("http://localhost:3001/premium");const q = (await quote.json()) as {payment: {tokenAccount: string;mint: string;amount: number;amountUSDC: number;cluster: string;};};if (quote.status !== 402) throw new Error("Expected 402 quote");const recipientTokenAccount = new PublicKey(q.payment.tokenAccount);const mint = new PublicKey(q.payment.mint);const amount = q.payment.amount;console.log("USDC Payment required:");console.log(` Recipient Token Account: ${q.payment.tokenAccount}`);console.log(` Mint (USDC): ${q.payment.mint}`);console.log(` Amount: ${q.payment.amountUSDC} USDC (${amount} smallest units)`);// 2) Get or create the payer's associated token accountconsole.log("\nChecking/creating associated token account...");const payerTokenAccount = await getOrCreateAssociatedTokenAccount(connection,payer,mint,payer.publicKey);console.log(` Payer Token Account: ${payerTokenAccount.address.toBase58()}`);// Check if payer has enough USDCconst balance = await connection.getTokenAccountBalance(payerTokenAccount.address);console.log(` Current Balance: ${balance.value.uiAmountString} USDC`);if (Number(balance.value.amount) < amount) {throw new Error(`Insufficient USDC balance. Have: ${balance.value.uiAmountString}, Need: ${q.payment.amountUSDC}`);}// 3) Check if recipient token account exists, create if notconsole.log("\nChecking recipient token account...");let recipientAccountExists = false;try {await getAccount(connection, recipientTokenAccount);recipientAccountExists = true;console.log(" ✓ Recipient token account exists");} catch (error) {console.log(" ⚠ Recipient token account doesn't exist, will create it");}// 4) Create USDC transfer transaction (but DON'T submit it)const { blockhash } = await connection.getLatestBlockhash();const tx = new Transaction({feePayer: payer.publicKey,blockhash,lastValidBlockHeight: (await connection.getLatestBlockhash()).lastValidBlockHeight});// Add create account instruction if neededif (!recipientAccountExists) {// We need to know the recipient wallet address to create the ATA// The server should provide this, so let's get it from the wallet address// Usually the server will already have the token account, but to be sure for the examples// lets create one.const recipientWallet = new PublicKey("seFkxFkXEY9JGEpCyPfCWTuPZG9WK6ucf95zvKCfsRX");const createAccountIx = createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction(payer.publicKey, // payerrecipientTokenAccount, // associated token account addressrecipientWallet, // ownermint // mint);tx.add(createAccountIx);console.log(" + Added create token account instruction");}// Add transfer instructionconst transferIx = createTransferInstruction(payerTokenAccount.address, // sourcerecipientTokenAccount, // destinationpayer.publicKey, // owneramount // amount in smallest units);tx.add(transferIx);// Sign the transaction (but don't send it, the server will do that)tx.sign(payer);// Serialize the signed transactionconst serializedTx = tx.serialize().toString("base64");console.log("\nTransaction created and signed (not submitted yet)");console.log(` Instructions: ${tx.instructions.length}`);// 4) Send X-Payment header with serialized transaction (x402 standard)const paymentProof = {x402Version: 1,scheme: "exact",network:q.payment.cluster === "devnet" ? "solana-devnet" : "solana-mainnet",payload: {serializedTransaction: serializedTx}};// Base64 encode the payment proofconst xPaymentHeader = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(paymentProof)).toString("base64");console.log("\nSending payment proof to server (server will submit transaction)...");const paid = await fetch("http://localhost:3001/premium", {headers: {"X-Payment": xPaymentHeader}});const result = (await paid.json()) as {data?: string;error?: string;paymentDetails?: {signature: string;amount: number;amountUSDC: number;recipient: string;explorerUrl: string;};};console.log("\nServer response:");console.log(result);// Display explorer link if payment was successfulif (result.paymentDetails?.explorerUrl) {console.log("\n🔗 View transaction on Solana Explorer:");console.log(result.paymentDetails.explorerUrl);}}run().catch(console.error);
Improvements
- Consider returning a JWT after payment so clients can reuse access briefly. ACK makes that quite easy.
- Make sure your keys do not leak and put them in environment variables.