Solanaネットワークと対話するには、トランザクションを送信する必要があります。トランザクションは、いくつかのフォームを含む封筒のようなものと考えることができます。各フォームはネットワークに何をすべきかを指示するinstructionです。トランザクションを送信することは、フォームが処理されるように封筒を郵送するようなものです。
以下の例は、2つのトランザクションの簡略版を示しています。最初のトランザクションが処理されると、単一のinstructionが実行されます。2番目のトランザクションが処理されると、順番に3つのinstructionが実行されます:まずinstruction 1、次にinstruction 2、そしてinstruction 3の順です。
トランザクションはアトミックです:単一のinstructionが失敗すると、トランザクション全体が失敗し、変更は一切発生しません。
2つのトランザクションを示す簡略図
Transaction
は以下の情報で構成されています:
signatures: 署名の配列message: 処理される instructions のリストを含むトランザクション情報
pub struct Transaction {#[wasm_bindgen(skip)]#[serde(with = "short_vec")]pub signatures: Vec<Signature>,#[wasm_bindgen(skip)]pub message: Message,}
 トランザクションの2つの部分を示す図
トランザクションの2つの部分を示す図
トランザクションの合計サイズ制限は
1232
バイトです。この制限には、signatures配列と
message構造体の両方が含まれます。
この制限は、一般的なインターネットインフラストラクチャでのパケットフラグメンテーションを回避するために設計されています。IPv6は9000バイト以上のMTUをサポートしていますが、ほとんどのインターネットルーターはデフォルトのMTUとして1500バイト(標準イーサネット)を使用しています。フラグメンテーションなしで単一のパケット内にトランザクションが収まるようにするため、Solanaは1280バイト(IPv6に必要な最小MTU)からネットワークヘッダー用の48バイト(IPv6の40バイト + フラグメント/UDPヘッダーの8バイト)を引いた、1232バイトのトランザクションサイズ制限を使用しています。
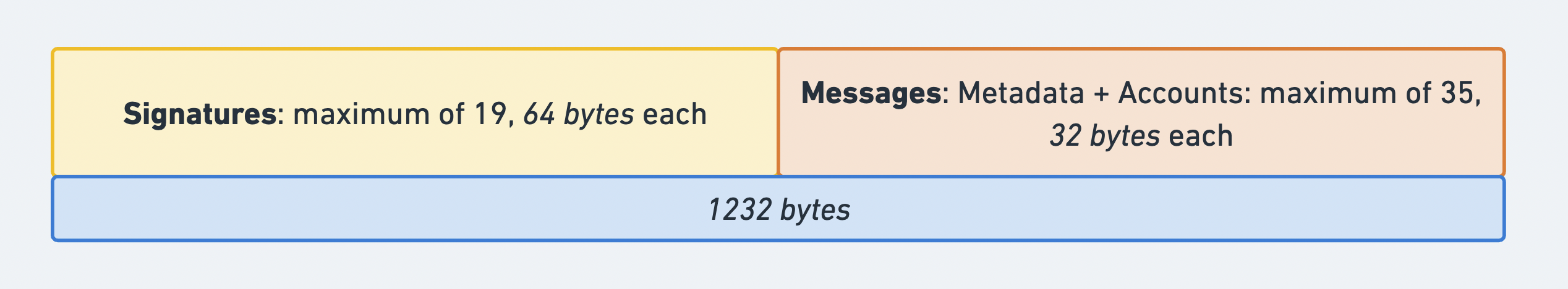 トランザクションフォーマットとサイズ制限を示す図
トランザクションフォーマットとサイズ制限を示す図
署名
トランザクションのsignatures配列にはSignature構造体が含まれます。各
Signature
は64バイトで、アカウントの秘密鍵でトランザクションのMessageに署名することで作成されます。トランザクションの instructions に含まれる各
署名者アカウントに対して署名を提供する必要があります。
最初の署名は、トランザクションの基本手数料を支払うアカウントに属し、トランザクション署名となります。このトランザクション署名を使用して、ネットワーク上でトランザクションの詳細を検索することができます。
メッセージ
トランザクションのmessageは
Message
構造体で、以下の情報を含みます:
header: メッセージヘッダーaccount_keys: トランザクションの instructions に必要な アカウントアドレスの配列recent_blockhash: トランザクションのタイムスタンプとして機能する ブロックハッシュinstructions: instructionsの配列
スペースを節約するため、トランザクションは各アカウントの権限を個別に保存しません。代わりに、アカウントの権限はheader
とaccount_keysを使用して決定されます。
pub struct Message {/// The message header, identifying signed and read-only `account_keys`.pub header: MessageHeader,/// All the account keys used by this transaction.#[serde(with = "short_vec")]pub account_keys: Vec<Pubkey>,/// The id of a recent ledger entry.pub recent_blockhash: Hash,/// Programs that will be executed in sequence and committed in/// one atomic transaction if all succeed.#[serde(with = "short_vec")]pub instructions: Vec<CompiledInstruction>,}
ヘッダー
メッセージのheaderは
MessageHeader
構造体です。以下の情報を含みます:
num_required_signatures: トランザクションに必要な署名の総数num_readonly_signed_accounts: 署名が必要な読み取り専用アカウントの総数num_readonly_unsigned_accounts: 署名が不要な読み取り専用アカウントの総数
pub struct MessageHeader {/// The number of signatures required for this message to be considered/// valid. The signers of those signatures must match the first/// `num_required_signatures` of [`Message::account_keys`].pub num_required_signatures: u8,/// The last `num_readonly_signed_accounts` of the signed keys are read-only/// accounts.pub num_readonly_signed_accounts: u8,/// The last `num_readonly_unsigned_accounts` of the unsigned keys are/// read-only accounts.pub num_readonly_unsigned_accounts: u8,}
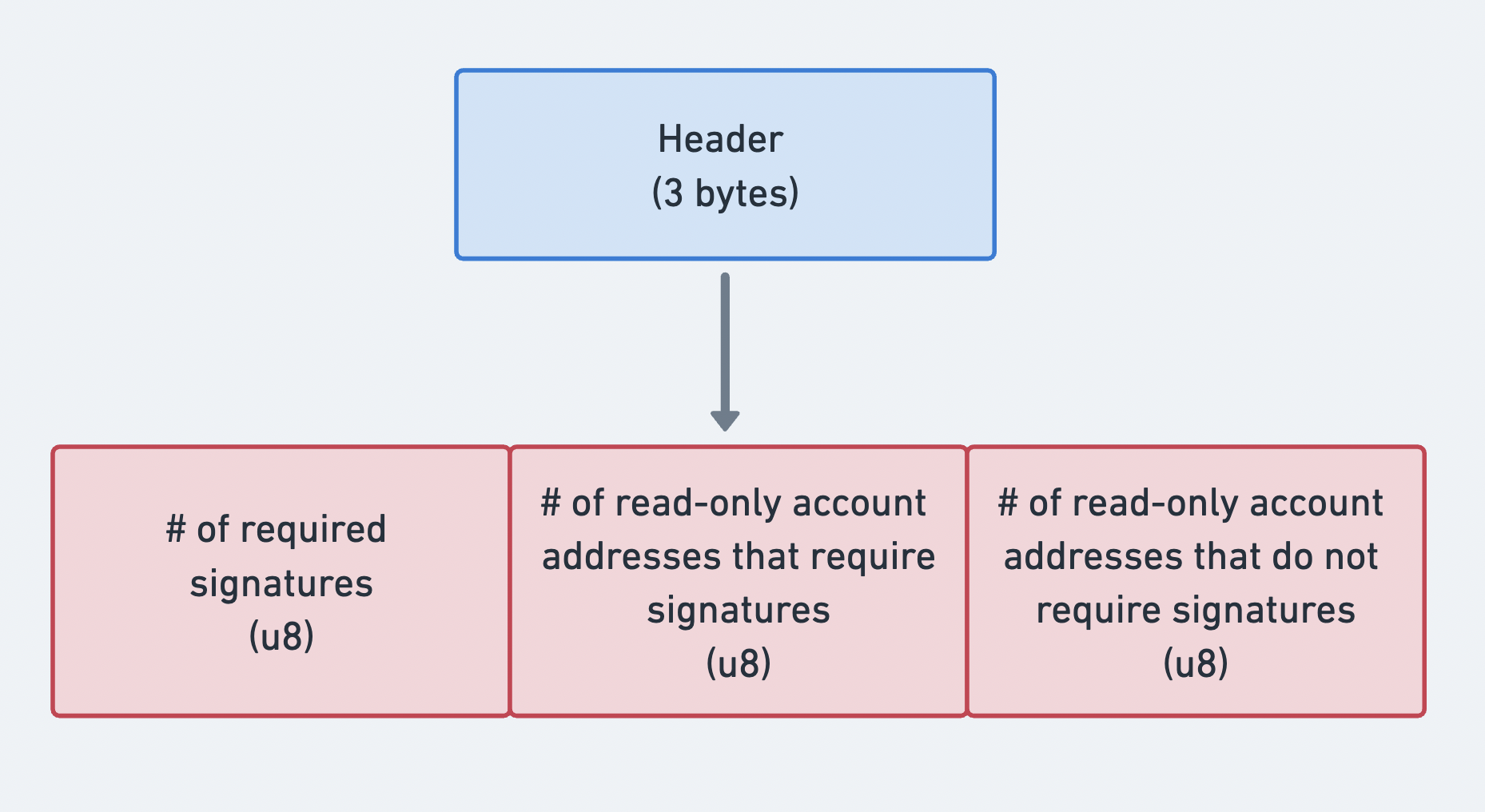 メッセージヘッダーの3つの部分を示す図
メッセージヘッダーの3つの部分を示す図
アカウントアドレス
メッセージのaccount_keysは、コンパクト配列形式で送信されるアカウントアドレスの配列です。配列の接頭辞はその長さを示します。配列内の各項目は公開鍵であり、instructionsで使用されるアカウントを指します。accounts_keys配列は完全であり、以下のように厳密に順序付けられている必要があります:
- 署名者 + 書き込み可能
- 署名者 + 読み取り専用
- 署名者でない + 書き込み可能
- 署名者でない + 読み取り専用
厳密な順序付けにより、account_keys配列をメッセージのheaderの情報と組み合わせて、各アカウントの権限を判断できます。
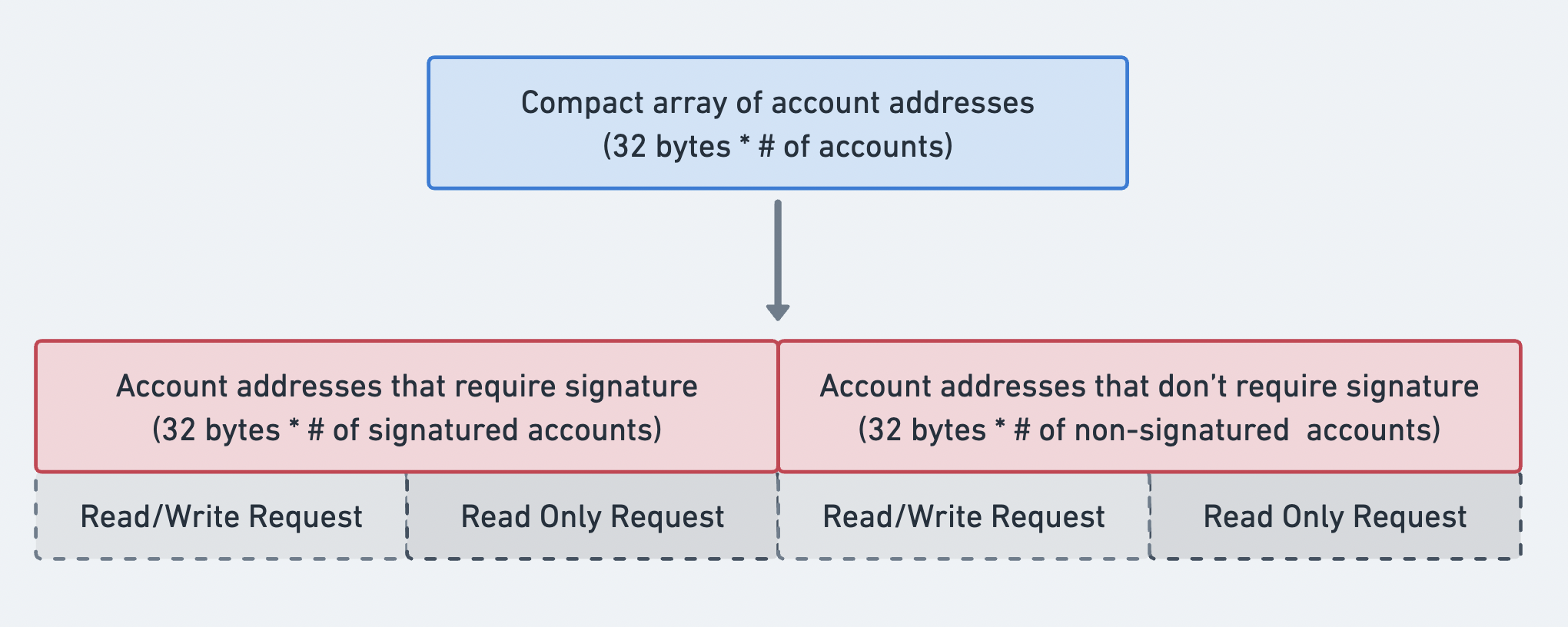 アカウントアドレス配列の順序を示す図
アカウントアドレス配列の順序を示す図
最新のブロックハッシュ
メッセージのrecent_blockhashは、トランザクションのタイムスタンプとして機能し、重複トランザクションを防ぐハッシュ値です。ブロックハッシュは150ブロック後に期限切れになります。(各ブロックが400msと仮定すると、1分に相当します。)ブロックの期限が切れると、トランザクションは期限切れとなり、処理できなくなります。
getLatestBlockhash
RPCメソッドを使用すると、現在のブロックハッシュと、そのブロックハッシュが有効な最後のブロック高を取得できます。
Instructions
メッセージのinstructionsは、コンパクト配列形式で送信される、処理されるすべてのinstructionsの配列です。配列の接頭辞はその長さを示します。配列内の各項目はCompiledInstruction構造体であり、以下の情報を含みます:
program_id_index:account_keys配列内のアドレスを指すインデックス。この値は、instructionを処理するプログラムのアドレスを示します。accounts:account_keys配列内のアドレスを指すインデックスの配列。各インデックスは、このinstructionに必要なアカウントのアドレスを指します。data: プログラム上で呼び出すinstructionを指定するバイト配列。また、instructionに必要な追加データも含みます。(例:関数の引数)
pub struct CompiledInstruction {/// Index into the transaction keys array indicating the program account that executes this instruction.pub program_id_index: u8,/// Ordered indices into the transaction keys array indicating which accounts to pass to the program.#[serde(with = "short_vec")]pub accounts: Vec<u8>,/// The program input data.#[serde(with = "short_vec")]pub data: Vec<u8>,}
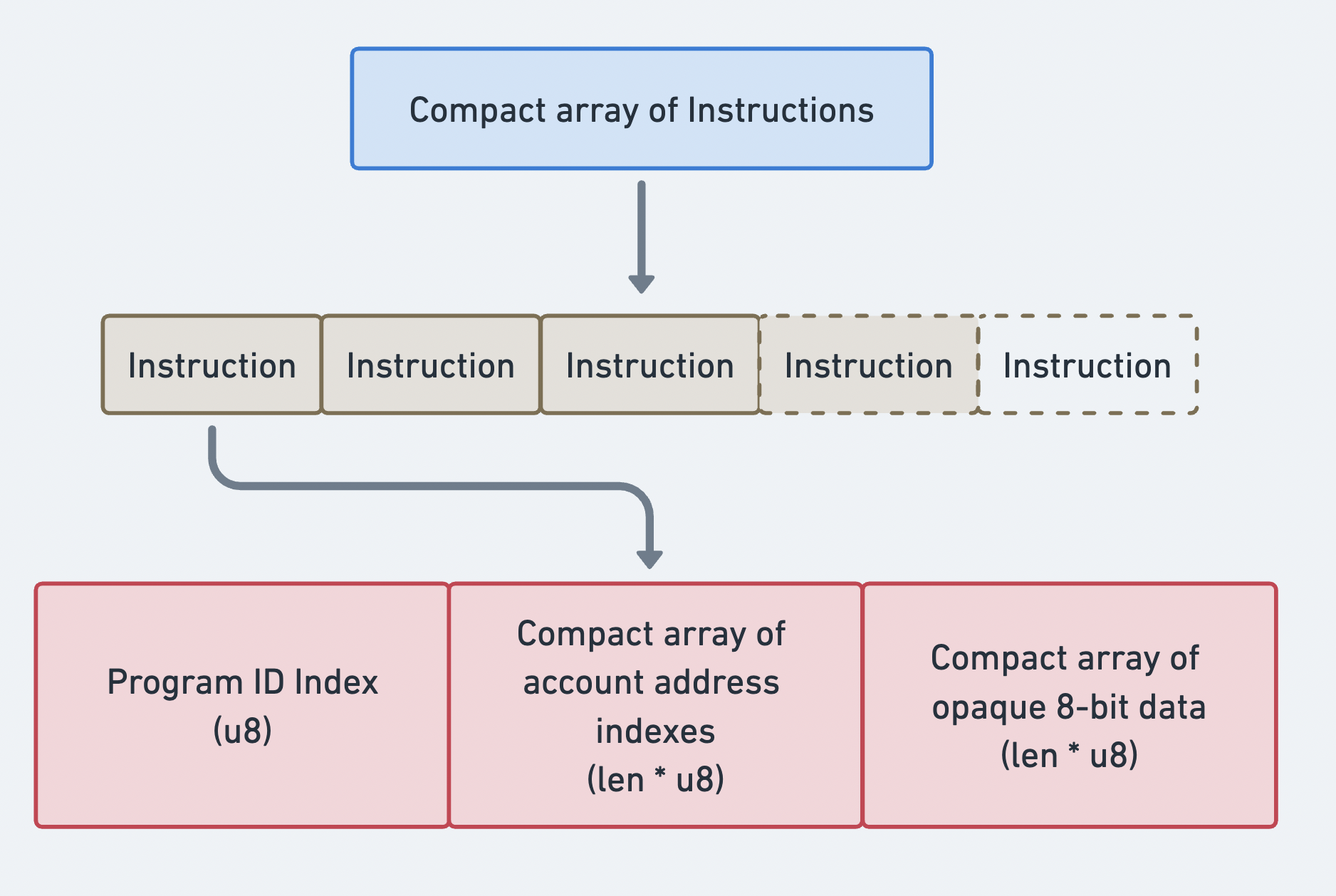 Instructionのコンパクト配列
Instructionのコンパクト配列
トランザクション構造の例
以下の例は、単一のSOL送金instructionを含むトランザクションの構造を示しています。
import {createSolanaRpc,generateKeyPairSigner,lamports,createTransactionMessage,setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner,setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash,appendTransactionMessageInstructions,pipe,signTransactionMessageWithSigners,getCompiledTransactionMessageDecoder} from "@solana/kit";import { getTransferSolInstruction } from "@solana-program/system";const rpc = createSolanaRpc("http://localhost:8899");const { value: latestBlockhash } = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();// Generate sender and recipient keypairsconst sender = await generateKeyPairSigner();const recipient = await generateKeyPairSigner();// Define the amount to transferconst LAMPORTS_PER_SOL = 1_000_000_000n;const transferAmount = lamports(LAMPORTS_PER_SOL / 100n); // 0.01 SOL// Create a transfer instruction for transferring SOL from sender to recipientconst transferInstruction = getTransferSolInstruction({source: sender,destination: recipient.address,amount: transferAmount});// Create transaction messageconst transactionMessage = pipe(createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }),(tx) => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(sender, tx),(tx) => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(latestBlockhash, tx),(tx) => appendTransactionMessageInstructions([transferInstruction], tx));const signedTransaction =await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(transactionMessage);// Decode the messageBytesconst compiledTransactionMessage =getCompiledTransactionMessageDecoder().decode(signedTransaction.messageBytes);console.log(JSON.stringify(compiledTransactionMessage, null, 2));
以下のコードは、前述のコードスニペットからの出力を示しています。 フォーマットはSDKによって異なりますが、 各instructionが同じ必要な情報を含んでいることに注目してください。
{"version": 0,"header": {"numSignerAccounts": 1,"numReadonlySignerAccounts": 0,"numReadonlyNonSignerAccounts": 1},"staticAccounts": ["HoCy8p5xxDDYTYWEbQZasEjVNM5rxvidx8AfyqA4ywBa","5T388jBjovy7d8mQ3emHxMDTbUF8b7nWvAnSiP3EAdFL","11111111111111111111111111111111"],"lifetimeToken": "EGCWPUEXhqHJWYBfDirq3mHZb4qDpATmYqBZMBy9TBC1","instructions": [{"programAddressIndex": 2,"accountIndices": [0, 1],"data": {"0": 2,"1": 0,"2": 0,"3": 0,"4": 128,"5": 150,"6": 152,"7": 0,"8": 0,"9": 0,"10": 0,"11": 0}}]}
トランザクションが送信された後、トランザクションシグネチャとgetTransaction RPCメソッドを使用して、その詳細を取得できます。レスポンスは以下のスニペットに似た構造になります。
Solana Explorerを使用してトランザクションを確認することもできます。
{"blockTime": 1745196488,"meta": {"computeUnitsConsumed": 150,"err": null,"fee": 5000,"innerInstructions": [],"loadedAddresses": {"readonly": [],"writable": []},"logMessages": ["Program 11111111111111111111111111111111 invoke [1]","Program 11111111111111111111111111111111 success"],"postBalances": [989995000, 10000000, 1],"postTokenBalances": [],"preBalances": [1000000000, 0, 1],"preTokenBalances": [],"rewards": [],"status": {"Ok": null}},"slot": 13049,"transaction": {"message": {"header": {"numReadonlySignedAccounts": 0,"numReadonlyUnsignedAccounts": 1,"numRequiredSignatures": 1},"accountKeys": ["8PLdpLxkuv9Nt8w3XcGXvNa663LXDjSrSNon4EK7QSjQ","7GLg7bqgLBv1HVWXKgWAm6YoPf1LoWnyWGABbgk487Ma","11111111111111111111111111111111"],"recentBlockhash": "7ZCxc2SDhzV2bYgEQqdxTpweYJkpwshVSDtXuY7uPtjf","instructions": [{"accounts": [0, 1],"data": "3Bxs4NN8M2Yn4TLb","programIdIndex": 2,"stackHeight": null}],"indexToProgramIds": {}},"signatures": ["3jUKrQp1UGq5ih6FTDUUt2kkqUfoG2o4kY5T1DoVHK2tXXDLdxJSXzuJGY4JPoRivgbi45U2bc7LZfMa6C4R3szX"]},"version": "legacy"}
Is this page helpful?