Solana 网络上的所有数据都存储在账户中。您可以将 Solana 网络视为一个包含单一账户表的公共数据库。账户与其地址之间的关系类似于键值对,其中键是地址,值是账户。
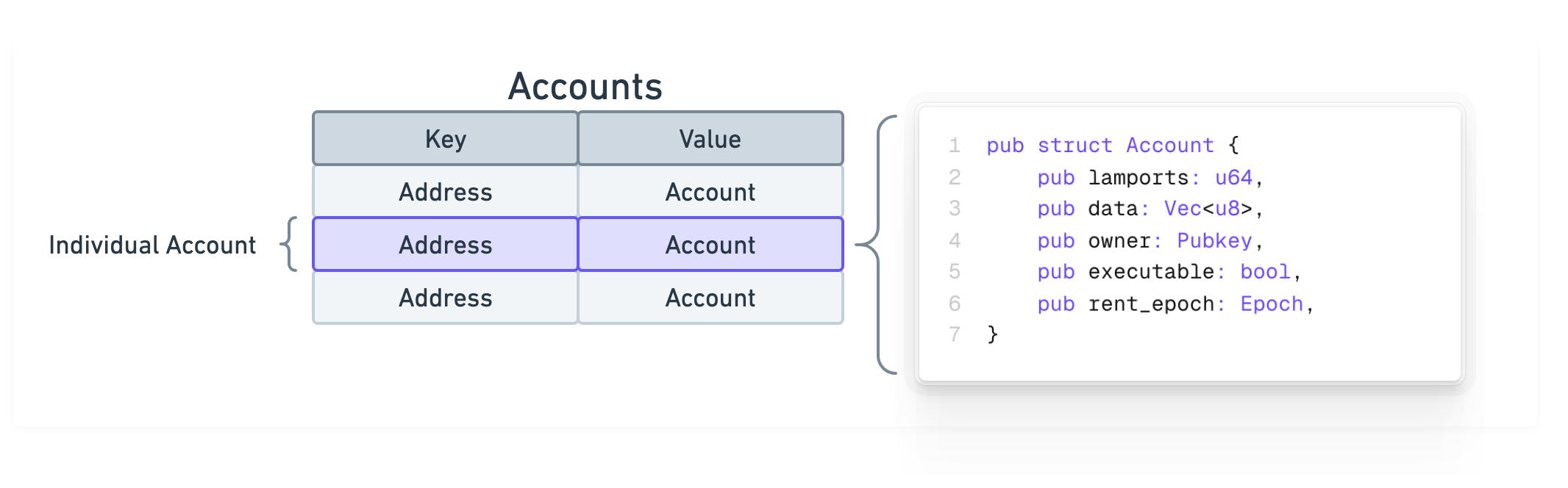 三个账户及其地址的示意图,包括账户结构定义。
三个账户及其地址的示意图,包括账户结构定义。
账户地址
账户地址是一个 32 字节的唯一 ID,用于在 Solana 区块链上定位账户。账户地址通常以 base58 编码字符串的形式显示。大多数账户使用 Ed25519 公钥 作为其地址,但这并不是强制性的,因为 Solana 还支持程序派生地址。
一个账户及其 base58 编码的公钥地址
公钥
下面的示例演示了如何使用 Solana SDK 创建一个 keypair。 Keypair 包含:
- 一个作为账户地址的公钥
- 一个用于签署交易的私钥
import { generateKeyPairSigner } from "@solana/kit";// Kit does not enable extractable private keysconst keypairSigner = await generateKeyPairSigner();console.log(keypairSigner);
程序派生地址
程序派生地址(PDA)是一个通过程序 ID 和一个或多个可选输入(种子)确定性派生的地址。下面的示例演示了如何使用 Solana SDK 创建一个程序派生地址。
import { Address, getProgramDerivedAddress } from "@solana/kit";const programAddress = "11111111111111111111111111111111" as Address;const seeds = ["helloWorld"];const [pda, bump] = await getProgramDerivedAddress({programAddress,seeds});console.log(`PDA: ${pda}`);console.log(`Bump: ${bump}`);
账户结构
每个
Account
最大容量为
10MiB,包含以下信息:
lamports:账户中的 lamports 数量data:账户数据owner:拥有该账户的 program 的 IDexecutable:指示账户是否包含可执行二进制文件rent_epoch:已弃用的 rent epoch 字段
pub struct Account {/// lamports in the accountpub lamports: u64,/// data held in this account#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde", serde(with = "serde_bytes"))]pub data: Vec<u8>,/// the program that owns this account. If executable, the program that loads this account.pub owner: Pubkey,/// this account's data contains a loaded program (and is now read-only)pub executable: bool,/// the epoch at which this account will next owe rentpub rent_epoch: Epoch,}
Lamports
数据
所有者
租赁 epoch
rent_epoch 字段已弃用。
过去,此字段用于跟踪账户何时需要支付租金。然而,此租金收取机制现已被弃用。
账户类型
账户分为两大类:
程序代码与其状态的分离是 Solana 账户模型的一个关键特性。(类似于操作系统,通常将程序和其数据分为不同的文件。)
程序账户
每个程序都由一个加载器程序拥有,用于部署和管理账户。当部署一个新的程序时,会创建一个账户来存储其可执行代码。这被称为程序账户。(为了简化,可以将程序账户视为程序本身。)
在下图中,你可以看到一个 loader program 被用来部署一个 program account。program
account 的 data 字段包含可执行的程序代码。
程序账户、其四个组成部分及其加载器程序的示意图
程序数据账户
使用 loader-v3 部署的 Programs 在其 data 字段中不包含程序代码。相反,它们的
data 指向一个单独的 program data account,其中包含程序代码。(见下图。)
一个程序账户及其数据。数据指向一个单独的程序数据账户
下面的示例获取了 Token Program account。请注意,executable 字段被设置为
true,表示该账户是一个 program。
import { Address, createSolanaRpc } from "@solana/kit";const rpc = createSolanaRpc("https://api.mainnet.solana.com");const programId = "TokenkegQfeZyiNwAJbNbGKPFXCWuBvf9Ss623VQ5DA" as Address;const accountInfo = await rpc.getAccountInfo(programId, { encoding: "base64" }).send();console.log(accountInfo);
数据账户
数据账户不包含可执行代码,而是用于存储信息。
程序状态账户
程序使用数据账户来维护其状态。为此,必须先创建一个新的数据账户。虽然创建程序状态账户的过程通常被抽象化,但了解其底层流程会很有帮助。
为了管理其状态,一个新程序必须:
- 调用 System Program 来创建一个账户。(然后 System Program 将所有权转移给新程序。)
- 根据其 instructions 初始化账户数据。
由程序账户拥有的数据账户示意图
下面的示例创建并获取一个由 Token 2022 程序拥有的 Token Mint 账户。
import {airdropFactory,appendTransactionMessageInstructions,createSolanaRpc,createSolanaRpcSubscriptions,createTransactionMessage,generateKeyPairSigner,getSignatureFromTransaction,lamports,pipe,sendAndConfirmTransactionFactory,setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner,setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash,signTransactionMessageWithSigners} from "@solana/kit";import { getCreateAccountInstruction } from "@solana-program/system";import {getInitializeMintInstruction,getMintSize,TOKEN_2022_PROGRAM_ADDRESS,fetchMint} from "@solana-program/token-2022";// Create Connection, local validator in this exampleconst rpc = createSolanaRpc("http://localhost:8899");const rpcSubscriptions = createSolanaRpcSubscriptions("ws://localhost:8900");// Generate keypairs for fee payerconst feePayer = await generateKeyPairSigner();// Fund fee payerawait airdropFactory({ rpc, rpcSubscriptions })({recipientAddress: feePayer.address,lamports: lamports(1_000_000_000n),commitment: "confirmed"});// Generate keypair to use as address of mintconst mint = await generateKeyPairSigner();// Get default mint account size (in bytes), no extensions enabledconst space = BigInt(getMintSize());// Get minimum balance for rent exemptionconst rent = await rpc.getMinimumBalanceForRentExemption(space).send();// Instruction to create new account for mint (token 2022 program)// Invokes the system programconst createAccountInstruction = getCreateAccountInstruction({payer: feePayer,newAccount: mint,lamports: rent,space,programAddress: TOKEN_2022_PROGRAM_ADDRESS});// Instruction to initialize mint account data// Invokes the token 2022 programconst initializeMintInstruction = getInitializeMintInstruction({mint: mint.address,decimals: 9,mintAuthority: feePayer.address});const instructions = [createAccountInstruction, initializeMintInstruction];// Get latest blockhash to include in transactionconst { value: latestBlockhash } = await rpc.getLatestBlockhash().send();// Create transaction messageconst transactionMessage = pipe(createTransactionMessage({ version: 0 }), // Create transaction message(tx) => setTransactionMessageFeePayerSigner(feePayer, tx), // Set fee payer(tx) => setTransactionMessageLifetimeUsingBlockhash(latestBlockhash, tx), // Set transaction blockhash(tx) => appendTransactionMessageInstructions(instructions, tx) // Append instructions);// Sign transaction message with required signers (fee payer and mint keypair)const signedTransaction =await signTransactionMessageWithSigners(transactionMessage);// Send and confirm transactionawait sendAndConfirmTransactionFactory({ rpc, rpcSubscriptions })(signedTransaction,{ commitment: "confirmed" });// Get transaction signatureconst transactionSignature = getSignatureFromTransaction(signedTransaction);console.log("Mint Address:", mint.address);console.log("Transaction Signature:", transactionSignature);const accountInfo = await rpc.getAccountInfo(mint.address).send();console.log(accountInfo);const mintAccount = await fetchMint(rpc, mint.address);console.log(mintAccount);
系统账户
并非所有账户在由 System Program 创建后都会被分配新的所有者。由 System Program 拥有的账户被称为系统账户。所有钱包账户都是系统账户,这使它们能够支付 交易手续费。
一个由 System Program 拥有的钱包,包含 1,000,000 lamports
当 SOL 第一次被发送到一个新地址时,会在该地址创建一个由 System Program 拥有的账户。
在下面的示例中,会生成一个新的 keypair 并用 SOL 进行资助。运行代码后,你可以看到账户的
owner 地址是 11111111111111111111111111111111(即
System Program)。
import {airdropFactory,createSolanaRpc,createSolanaRpcSubscriptions,generateKeyPairSigner,lamports} from "@solana/kit";// Create a connection to Solana clusterconst rpc = createSolanaRpc("http://localhost:8899");const rpcSubscriptions = createSolanaRpcSubscriptions("ws://localhost:8900");// Generate a new keypairconst keypair = await generateKeyPairSigner();console.log(`Public Key: ${keypair.address}`);// Funding an address with SOL automatically creates an accountconst signature = await airdropFactory({ rpc, rpcSubscriptions })({recipientAddress: keypair.address,lamports: lamports(1_000_000_000n),commitment: "confirmed"});const accountInfo = await rpc.getAccountInfo(keypair.address).send();console.log(accountInfo);
Sysvar 账户
Sysvar 账户存在于预定义的地址,并提供对集群状态数据的访问。它们会动态更新网络集群的相关数据。查看完整列表:Sysvar Accounts。
下面的示例从 Sysvar Clock 账户中获取并反序列化数据。
import { createSolanaRpc } from "@solana/kit";import { fetchSysvarClock, SYSVAR_CLOCK_ADDRESS } from "@solana/sysvars";const rpc = createSolanaRpc("https://api.mainnet.solana.com");const accountInfo = await rpc.getAccountInfo(SYSVAR_CLOCK_ADDRESS, { encoding: "base64" }).send();console.log(accountInfo);// Automatically fetch and deserialize the account dataconst clock = await fetchSysvarClock(rpc);console.log(clock);
Is this page helpful?